Floatation devices are essential in industrial projects, supporting and stabilizing pipes and hoses in various environments. Choosing the correct type of floatation device can significantly impact the efficiency and safety of your operations. This blog aims to compare hose floats and pipe floats, helping you determine which floatation solution best suits your specific project needs.
Understanding Hose Floats
Definition and Description of Hose Floats
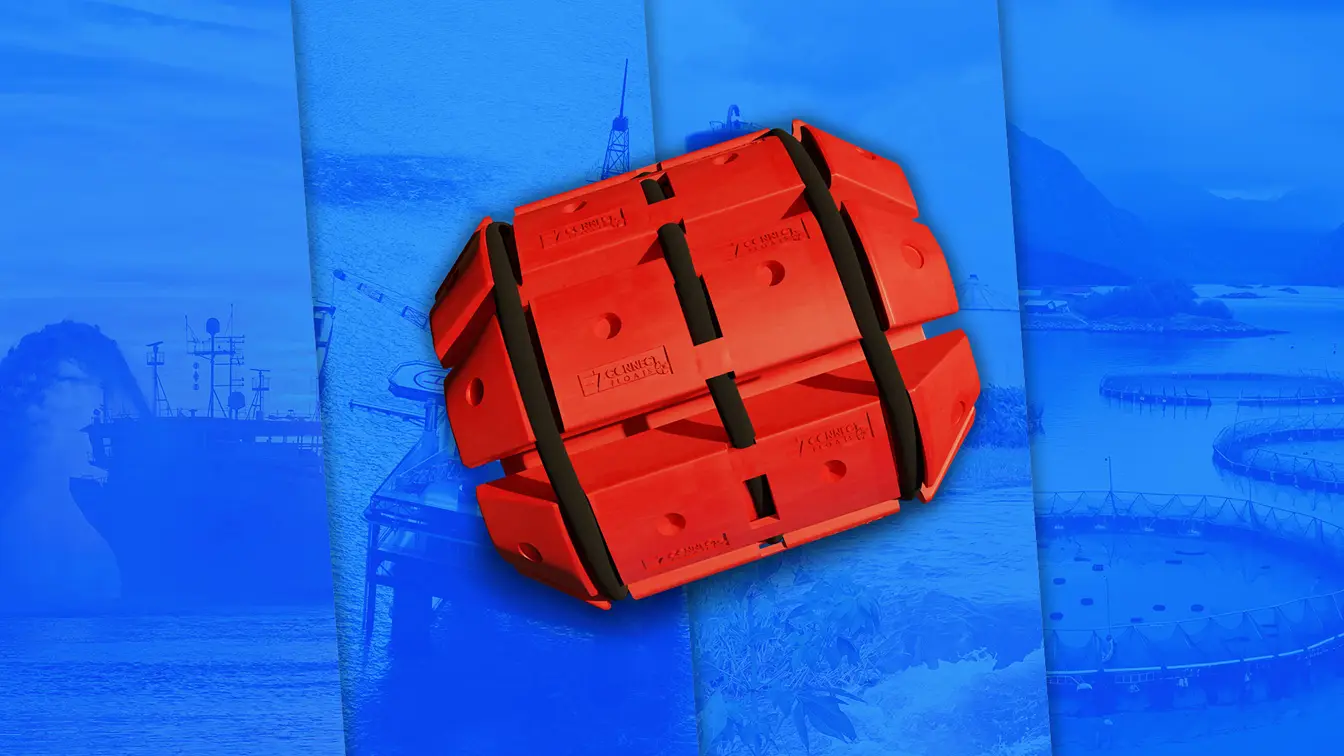
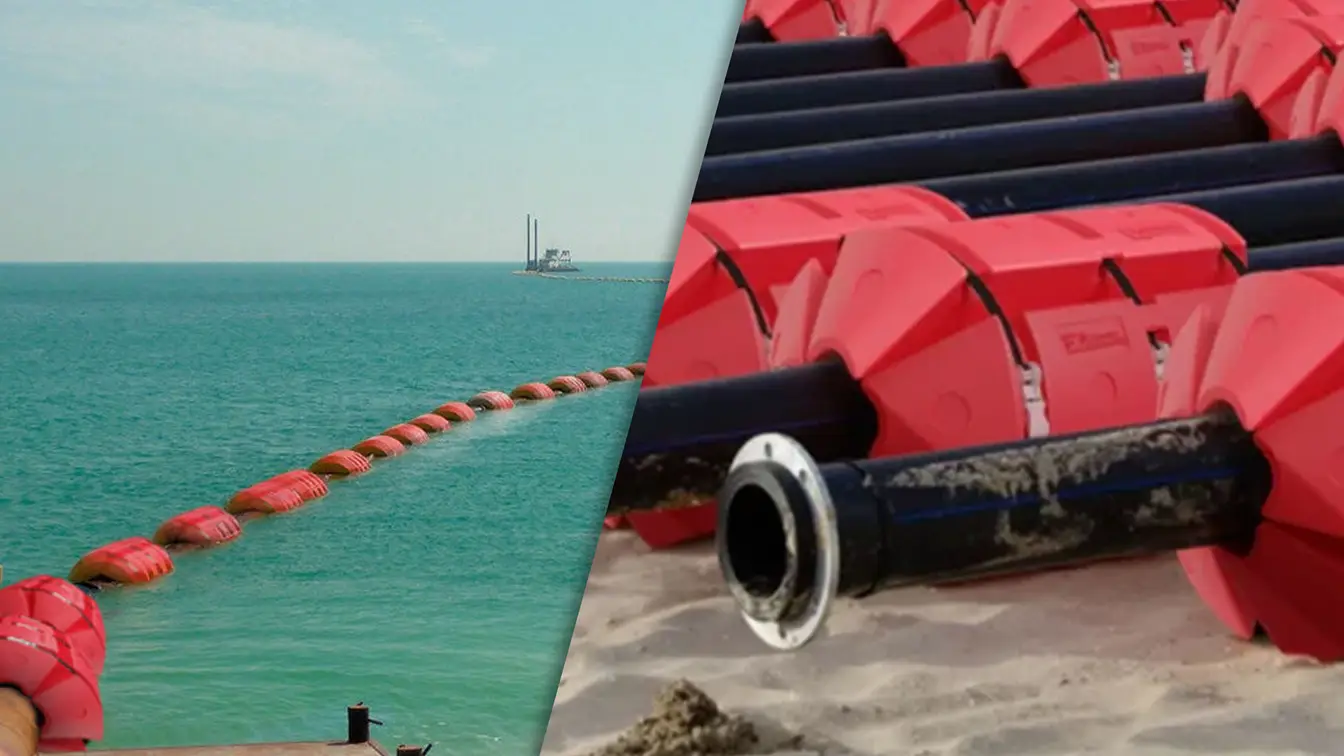
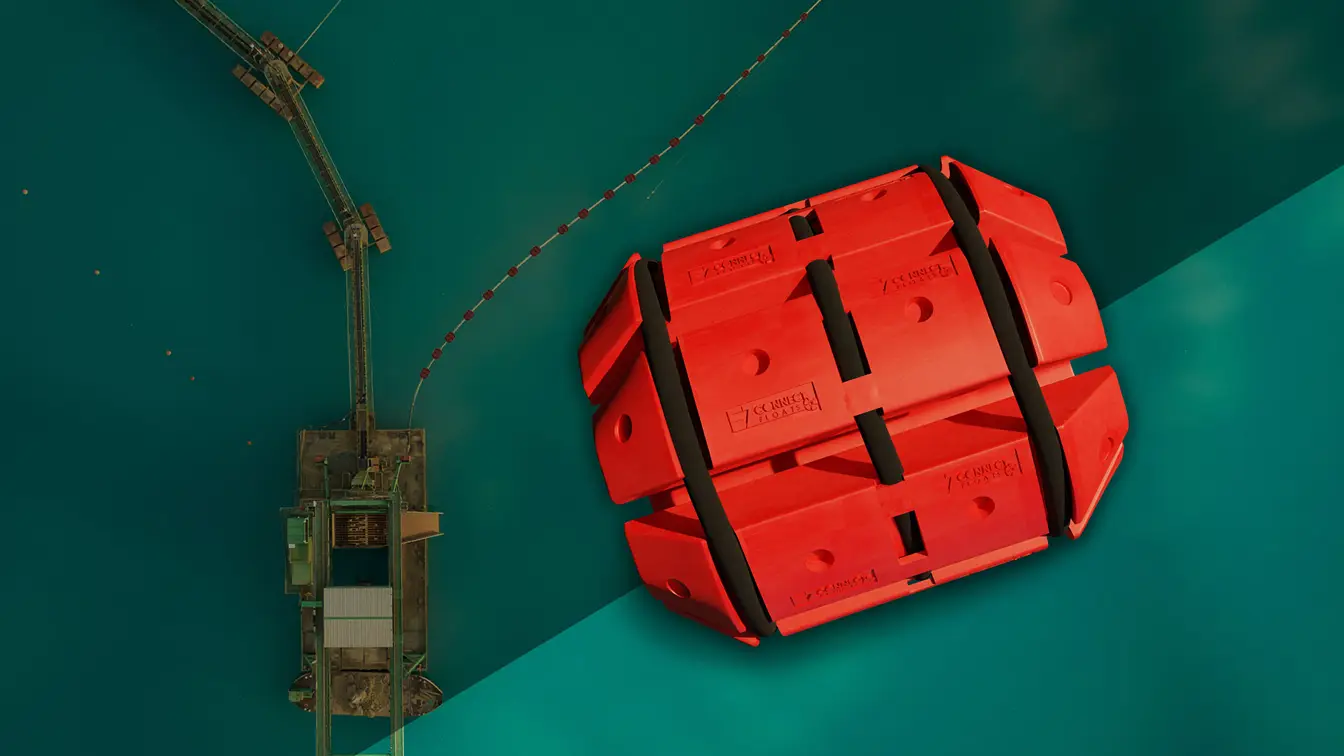
Hose floats are specialized buoyant devices that keep hoses afloat in various industrial applications. They are typically attached to the hose at regular intervals, providing consistent buoyancy and preventing the hose from sinking. Hose floats are essential in environments where hoses are used in water or other fluids, ensuring that the hoses remain operational and free from damage caused by submersion.
Standard Materials and Designs Used in Hose Floats
Hose floats are constructed using materials that offer buoyancy, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Some of the most common materials include:
- Polyethylene (PE): This is a widely used material due to its lightweight nature and excellent buoyancy. PE is resistant to various chemicals, making it suitable for use in different industrial settings.
- Polyurethane (PU): Known for its durability and resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure, PU is often used in more demanding environments.
- Foam-filled Plastics: These floats have a durable outer shell filled with foam, providing additional buoyancy and structural integrity. They are instrumental in rough conditions where extra support is required.
The designs of hose floats vary, but they generally fall into a few common types:
- Cylindrical Floats: These tube-like floats attach around the hose, providing even buoyancy along the hose’s length.
- Donut-shaped Floats: These floats encircle the hose and are often used in environments where the hose needs to pass through the float freely while remaining buoyant.
- Modular Floats: These are designed in segments that can be added or removed as needed, providing customizable buoyancy based on specific project requirements.
Typical Applications and Industries Utilizing Hose Floats
Hose floats are employed in various industries that use them in fluid environments. Some typical applications and industries include:
- Dredging and Marine Construction: In dredging operations, hose floats keep the discharge hoses afloat, preventing them from getting buried under sediments and ensuring continuous operation. In marine construction, they support hoses transporting materials to and from construction sites.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Hose floats are crucial in offshore oil and gas operations, where hoses transfer oil, gas, and other fluids. Floats ensure these hoses remain operational, reducing the risk of damage and downtime.
- Environmental Management: Hose floats are used in various ecological management applications, such as supporting hoses in floating silt curtains and oil spill containment systems. They ensure these hoses remain at the surface, effectively containing and managing spills and siltation.
- Agriculture and Aquaculture: In agriculture, hose floats can keep hoses afloat in ponds or canals by supporting irrigation systems. In aquaculture, they support hoses used in feeding systems or water aeration, ensuring they remain operational and do not sink.
Hose floats are essential in these industries, providing the necessary support and stability to ensure that hoses function efficiently and effectively in fluid environments. Their selection depends on the project’s specific requirements, including the type of hose used, the environmental conditions, and the desired level of buoyancy.
Understanding Pipe Floats
Definition and Description of Pipe Floats
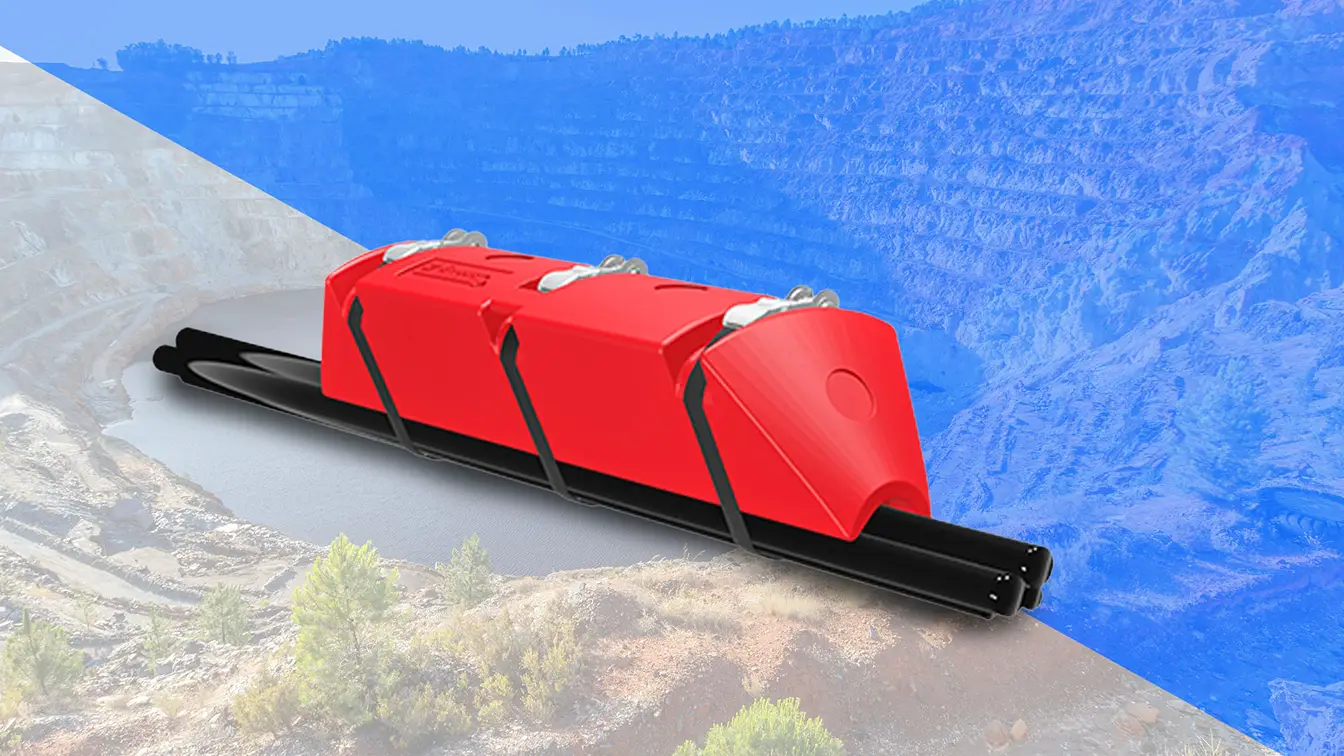
Pipe floats are buoyant devices that support pipes in various industrial and marine environments. They are attached to the pipes at regular intervals, ensuring that they remain afloat and properly aligned. By providing buoyancy, pipe floats prevent pipes from sinking and damaging themselves, thereby maintaining the efficiency and safety of operations.
Standard Materials and Designs Used in Pipe Floats
Pipe floats are made from materials that offer durability, buoyancy, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. The most common materials used in the manufacturing of pipe floats include:
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): HDPE is a popular choice due to its high strength-to-density ratio, chemical resistance, and UV stability. It is durable and suitable for long-term use in various industrial applications.
- Foam-filled HDPE: These floats have an HDPE outer shell filled with closed-cell foam. This combination provides additional buoyancy and ensures the float remains effective even if the outer shell is punctured.
The designs of pipe floats typically focus on providing secure and stable support for pipes. Common designs include:
- Clamp-on Floats: These split floats can be clamped around the pipe and secured with bolts or straps. They are easy to install and remove, making them versatile for different pipe sizes and applications.
- Molded Halves: Similar to clamp-on floats, these floats come in two molded halves that encircle the pipe. They are often bolted together to provide a secure fit and consistent buoyancy.
- Segmented Floats: These floats are designed in modular segments that can be linked together to provide customized buoyancy based on the project’s specific needs.
Typical Applications and Industries Utilizing Pipe Floats
Pipe floats are used in various industries where pipes must be kept afloat in fluid environments. Some typical applications and industries include:
- Mining and Mineral Processing: In mining operations, pipe floats support slurry pipelines transporting mineral concentrates and tailings. They ensure the pipelines remain operational, reducing the risk of blockages and damage.
- Water Treatment and Supply: Pipe floats are employed in water treatment plants to support intake and discharge pipelines. They ensure that these pipelines remain at the surface, facilitating the efficient water flow to and from treatment facilities.
- Marine and Offshore Construction: In marine construction projects, pipe floats support pipelines that transport materials to and from construction sites. They are also essential in offshore drilling operations, where they keep pipelines afloat and aligned.
- Dredging: In dredging operations, pipe floats support pipelines transporting dredged materials from the seabed to the shore or disposal sites. They ensure that these pipelines remain afloat, prevent them from being buried under sediment, and ensure continuous operation.
Pipe floats are crucial in these industries, providing the necessary buoyancy and stability to ensure pipelines function efficiently and safely. Their selection depends on various factors, including the type of pipe used, the environmental conditions, and the project’s specific requirements. By understanding the materials and designs of pipe floats, industries can choose the most suitable floatation solution to meet their operational needs.
Critical Differences Between Hose Floats and Pipe Floats
Design and Structure
Hose Floats:
- Typically smaller, cylindrical, or donut-shaped.
- Lighter and more flexible, suitable for different hose sizes and applications.
Pipe Floats:
- Larger, robust designs for enhanced stability.
- Structured to support heavier and larger diameter pipes, providing superior buoyancy.
Material Composition
Hose Floats:
- Made from lightweight materials like PE and PU.
- Suitable for environments requiring flexibility and ease of handling.
Pipe Floats:
- Constructed from durable materials like HDPE and foam-filled HDPE.
- It is designed to withstand harsh conditions and provide long-term durability.
Application Scenarios
Hose Floats:
- It is ideal for temporary or mobile applications.
- Commonly used in environmental management and offshore oil spill containment.
Pipe Floats:
- Best suited for permanent or semi-permanent installations.
- Widely used in mining, marine construction, and water treatment projects.
Installation and Maintenance
Hose Floats:
- It is easier to install due to its lightweight and simple design.
- They require minimal maintenance, making them suitable for temporary setups.
Pipe Floats:
- Installation can be more complex due to size and weight.
- Designed for long-term use with durable materials, reducing maintenance frequency.
Cost Considerations
Hose Floats:
- Lower initial costs due to more straightforward design and materials.
- Economical for short-term projects with limited budgets.
Pipe Floats:
- Higher initial investment, but cost-effective in the long run.
- Suitable for large-scale projects where long-term performance is crucial.
Advantages of Hose Floats
Flexibility and Adaptability
Hose floats can be easily adjusted and repositioned, making them highly flexible and adaptable to various conditions.
Lightweight and Easy to Handle
Their lightweight design simplifies installation and reduces labor costs, making them an efficient choice for many projects.
Specific Scenarios Where Hose Floats Excel
Hose floats are particularly effective in temporary and mobile applications, such as environmental management tasks requiring frequent adjustments.
Advantages of Pipe Floats
Enhanced Stability and Support
Pipe floats provide superior stability and support for larger pipelines, ensuring they remain afloat and operational in challenging environments.
Robustness and Durability
Constructed from durable materials, pipe floats can withstand harsh environmental conditions and heavy loads, making them suitable for long-term use.
Specific Scenarios Where Pipe Floats Excel
Pipe floats are ideal for permanent installations in mining, marine construction, and water treatment industries, where stability and durability are paramount.
Pros and Cons Summary
Hose Floats
Pros:
- Flexible and adaptable.
- Lightweight and easy to handle.
- Cost-effective for temporary applications.
Cons:
- Less stable for heavy-duty or permanent applications.
- It may require more frequent adjustments.
Pipe Floats
Pros:
- Extremely stable and supportive.
- Durable and long-lasting.
- Suitable for heavy-duty and permanent installations.
Cons:
- Higher initial cost.
- More complex installation process.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
This comparison highlights the differences between hose and pipe floats, focusing on design, materials, applications, installation, maintenance, and costs.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Right Floatation Solution
Choosing the right floatation solution depends on your project’s specific needs. Hose floats offer flexibility and ease of use for temporary and mobile applications, while pipe floats provide enhanced stability and durability for permanent installations.
Emphasis on Evaluating Project-Specific Needs
To make the best decision, evaluate your project’s requirements, including environmental conditions, budget constraints, and the expected duration of use. Considering these factors, you can select the floatation solution that best meets your project’s demands, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.